Synchronous Motors Objectives Part 03
41 . Which synchronous motor will be smallest in size 5 HP 375 rpm (small HP and rpm)
42 . A synchronous machine has its field winding on the stator and armature winding on the rotor, under steady running conditions, the air gap filed remains stationary with respect to stator
43 . If the field of a synchronous motor is under-excited, the power factor will be lagging
44 . The name plate of a induction motor reads 3 phase, 400 V, 50 Hz, 0.8 Hz of lagging, 1440 rpm. On similar lines the name plate of a synchronous motor should read 3 phase, 400 V, 50 Hz, 0.8 Hz of leading, 1500 rpm
45 . In which coil the emf generated will be more, for given flux distribution and number of turns full pitch coil
46 . In synchronous motor which loss does not vary with load windage losses
47 . In a 3 phase, 400 V, 50 Hz, salient pole synchronous motor, the maximum power is obtained when the load angle is less than 90 degree
48 . A high starting torque synchronous motor has simplex rotor, phase wound damper and five slip rings
49 . In a 3-phase synchronous motor the magnitude of filed flux remains constant at all loads
50 . The parameter connected with the operation of synchronous motor are speed, power factor and armature current. When the excitation of the motor is varied, power factor and armature current varied
51 . A 3 phase, 400 V, 50 Hz salient pole synchronous motor is running on no load. If there is a break in the excitation winding of the motor the motor will stop
52 . In the below figure, variation of synchronous reactance for synchronous motor with field current is represented by Curve D
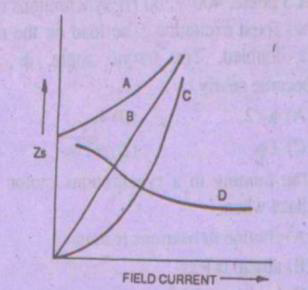
53 . A synchronous motor is said to be floating when it operates on no load and without losses
54 . The negative phase sequence in a three-phase synchronous motor exist when unbalanced voltage is supplied
55 . The field winding of a synchronous motor is shorted. A variable voltage is now supplied to the stator. The result will be motor will rotate at a speed which is less than the synchronous speed
56 . In a 3-phase synchronous motor, the poles lead ꝕr
57 . A 3-phase synchronous motor is running clockwise. In case the direction of its field current is reversed the motor will continue to run in the same direction
58 . The speed regulation of a 3-phase synchronous motor is zero
59 . When E is supplied voltage and R is the rotor resistance per phase, the mechanical power developed by synchronous motor per phase is given by V2 / 4R
60 . In a synchronous motor, the synchronizing power comes into action when rotor speed is either less or more than synchronous speed
